Risk with external advanced technology
? MethaneSat: abnormal orientation.
Current Mission StatusLoss of Contact: On June 20, 2025, mission operations lost contact with the satellite. Despite hundreds of attempts to restore communication, the satellite was declared irrecoverable on July 1, 2025.Investigation Findings: An official report released in November 2025 concluded that a "solitary event" likely caused a failure in either the avionics unit or the electrical power subsystem. High-resolution optical imagery confirmed the spacecraft was intact but in an abnormal orientation.Mission Duration: The satellite operated for 15 months of its originally planned five-year lifespan.
? MAVEN: recent partial tracking data suggests the satellite may be rotating unexpectedly and its orbit may have changed.
MAVEN similar failure Current Recovery EffortsLoss of Signal: Contact was lost on December 6, 2025, after the spacecraft passed behind Mars. While health data from December 4 showed normal operations, recent partial tracking data suggests the satellite may be rotating unexpectedly and its orbit may have changed.Visual Search: On December 16 and 20, 2025, the Curiosity rover used its Mastcam instrument to try and photograph MAVEN in its expected orbit, but the spacecraft was not detected.Solar Conjunction Delay: Active recovery attempts are currently paused due to Mars solar conjunction, which begins on December 29, 2025. During this time, Earth and Mars are on opposite sides of the Sun, making radio communication impossible. NASA expects to resume recovery efforts after January 16, 2026
? Satellite 35956: height drop, exploded.
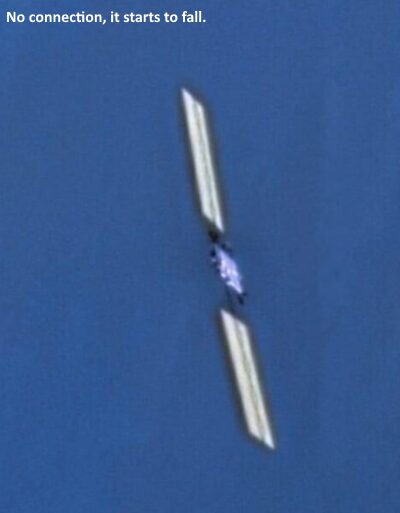
On December 18, 2025, the WorldView-3 satellite operated by U.S. satellite imaging company Vantor captured an image of a Starlink satellite that had lost contact with Earth. Photo courtesy of Vantor.

- Galileo (EU): A significant constellation degradation occurred between May 12 and May 19, 2025. While service was partially restored by June, transparency concerns remain regarding the full extent of the impact on satellite health and integrity.
- BeiDou-3 (China): Analysis through mid-2025 identified systematic rotation errors in broadcast ephemerides for its Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites. These orientation-related errors contributed to 3D positioning inaccuracies of approximately 19.3 cm before specialized corrections were applied.
- IRNSS/NavIC (India): The I03 satellite has shown notable orientation and ranging issues, specifically with its User Range Accuracy (URA). There is no reliable prediction available for more than one-third of its total broadcast data as of recent analysis.
- Mass Deorbit Event (January 2025): Approximately 120 Starlink satellites fell from orbit in January 2025 due to unidentified reliability issues that prevented them from maintaining stable orientations.
- Tumbling/Breakup (December 2025): Reports from late 2025 identified at least one Starlink satellite tumbling uncontrollably after a partial breakup in orbit, posing a risk of becoming un-trackable space debris.
- Falcon 9 Orbit Error (July 2024): A rocket failure left 20 satellites in the "wrong" orbit; while not a direct attitude control failure, it forced the satellites into altitudes where atmospheric drag compromised their ability to orient correctly.
- Affected Missions: GRACE-C/D, SWARM-A/B/C, and Sentinel-3A/B.
- Sentinel-2: As of June 2025, specific pixel-level errors in imaging data were reported, which are linked to the satellite's orientation and sensor alignment.
- Atmospheric Drag Impact: Satellites in Very Low Earth Orbit (VLEO) continue to face stability challenges due to high aerodynamic drag, which can cause uncommanded tumbling if not actively compensated by advanced control algorithms.
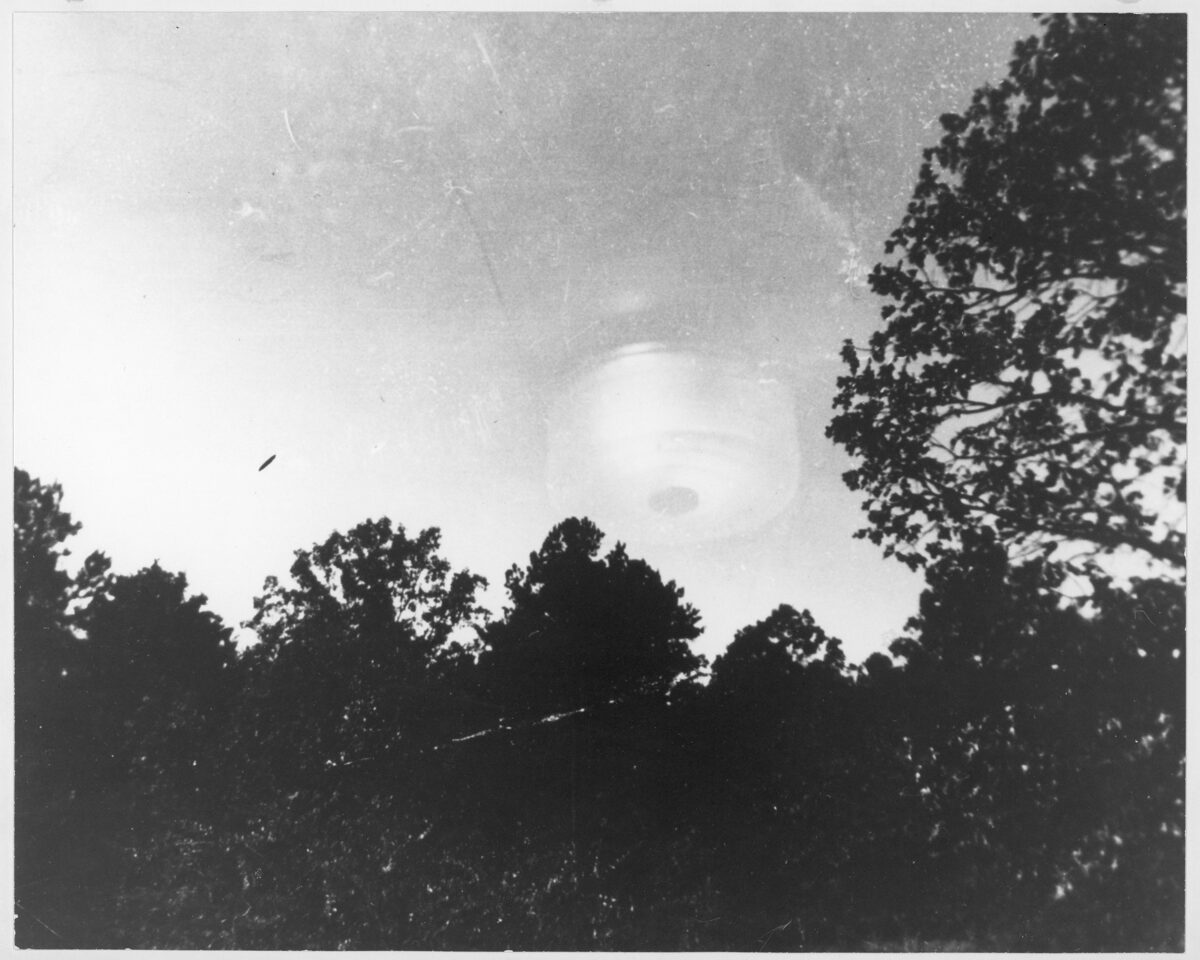
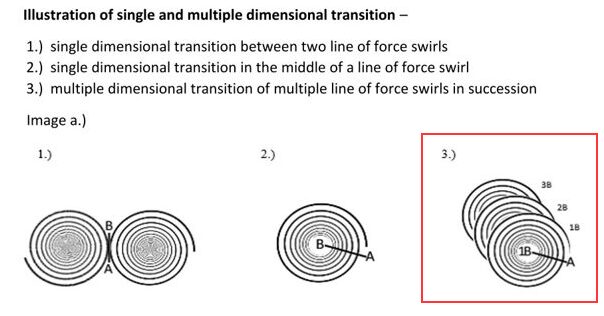
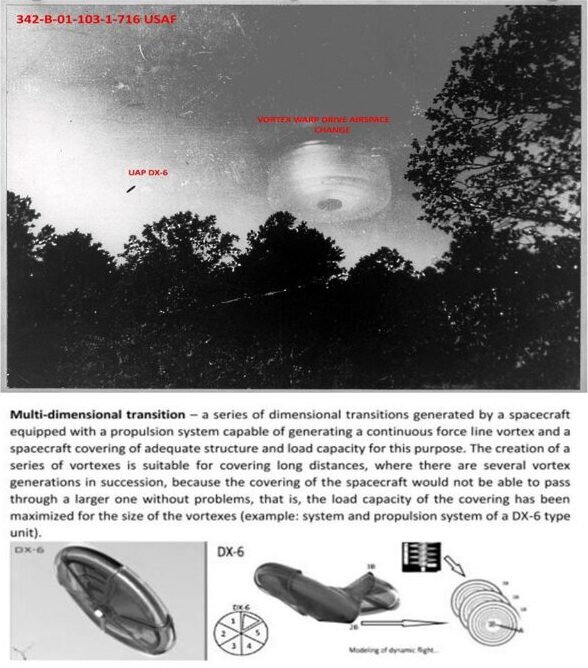
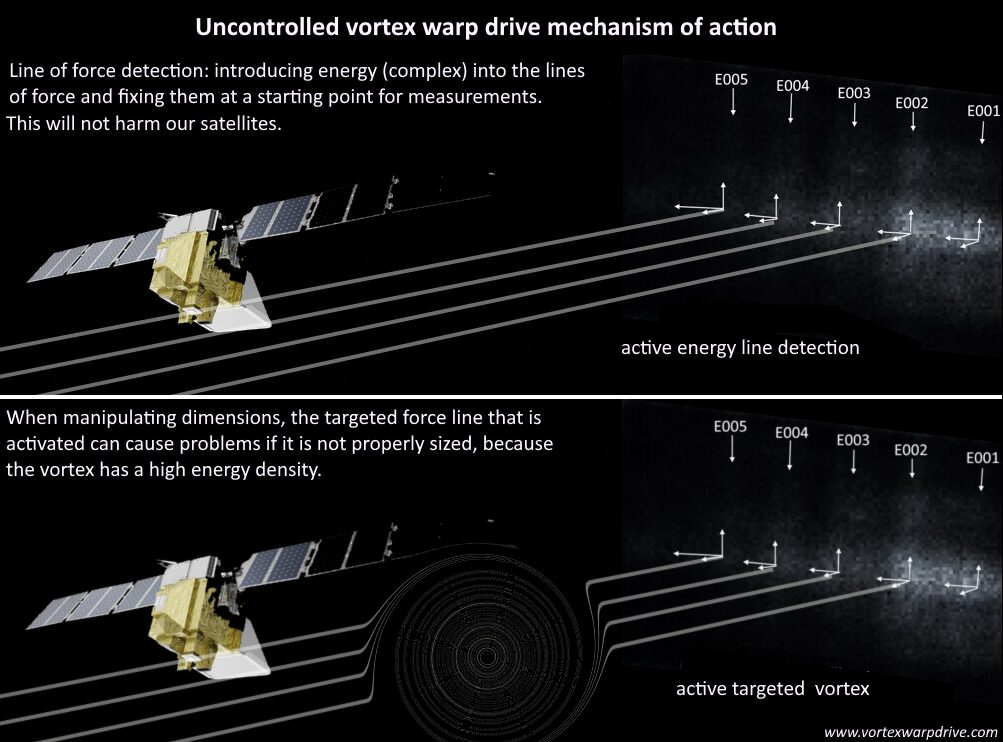
Illustration of a vortex from an archival military document.